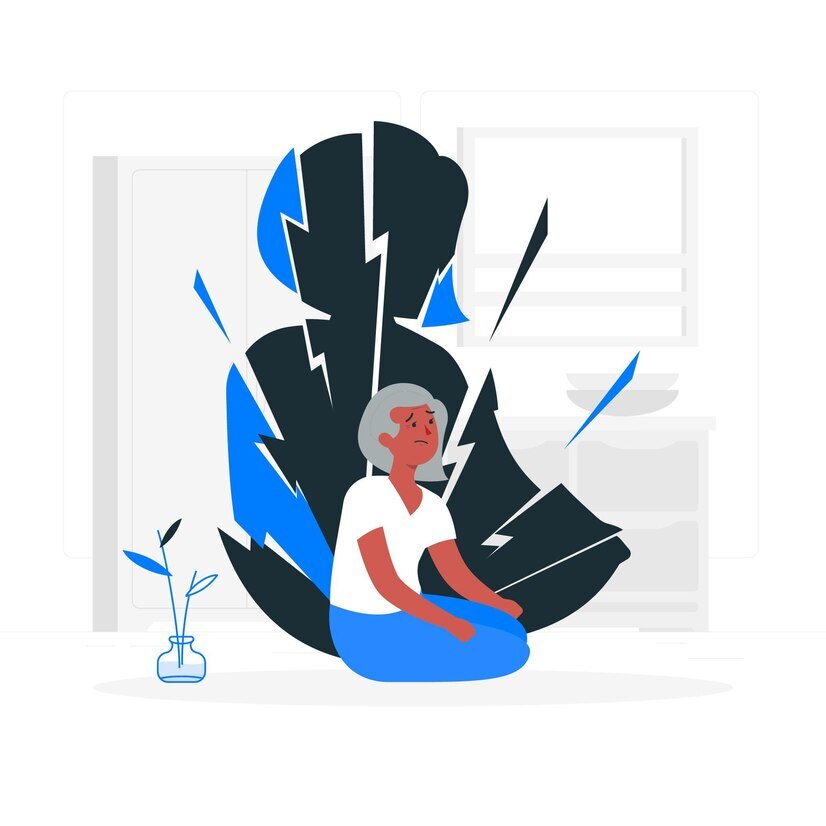
Chronic trauma refers to repeated and prolonged exposure to distressing and often overwhelming events or situations. Unlike acute trauma, which stems from a single traumatic incident, chronic trauma occurs over an extended period. This can include experiences such as ongoing abuse, neglect, or living in consistently unsafe environments. Prolonged trauma can have profound and lasting effects on a person’s mental, emotional, and physical well-being, often requiring specialized support and therapeutic interventions for healing and recovery.
Is chronic trauma the same as PTSD?
Chronic trauma and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) share some similarities but are not the same. Chronic trauma refers to repeated exposure to distressing events over an extended period, which can result in a range of emotional and psychological symptoms. On the other hand, PTSD is a specific mental health condition that can develop following a single traumatic incident or a series of traumas.
Causes of Chronic Trauma?
For someone dealing with chronic trauma, consulting the “Best psychologist in India” can be a crucial step towards healing and recovery.
- Childhood Abuse: Physical, emotional, or sexual abuse during childhood can lead to Prolonged trauma.
- Neglect: Ongoing neglect or emotional deprivation in childhood or adulthood can be traumatic.
- War and Conflict: Living in war-torn regions or being exposed to ongoing conflict can lead to Sustained trauma.
- Natural Disasters: Repeated exposure to natural disasters, such as hurricanes, earthquakes, or floods, can lead to Continuous trauma.
- Chronic Illness: Coping with a long-term or terminal illness, or being a caregiver for someone with a chronic illness, can be traumatic.
- Discrimination: Persistent experiences of discrimination based on factors like race, gender, sexual orientation, or religion can lead to Ongoing trauma.
- Human Trafficking: Individuals who have been trafficked or exploited often experience ongoing traumatic situations.
- Institutionalized Abuse: Traumatic experiences can result from being in environments with systemic abuse, such as some foster care systems, prisons, or residential institutions.
For individuals dealing with Sustained trauma and its impact on their relationships, “Marriage counselling” offers professional support to navigate and heal together.
Exploring the Symptoms of Chronic Trauma
The symptoms of chronic trauma are diverse and can significantly impact an individual’s mental, emotional, and physical well-being. Here is a more in-depth exploration of the common symptoms associated with Recurrent trauma:
- Recurrent Flashbacks: Individuals may experience intrusive and distressing memories of the traumatic events, which can feel as though they are reliving the trauma.
- Emotional Numbing: Ongoing trauma can lead to a sense of emotional detachment, where individuals feel disconnected from their own feelings, leading to a diminished capacity for joy, love, or happiness.
- Avoidance: A persistent effort to avoid reminders of the traumatic events, including people, places, or situations that trigger distressing memories.
- Hyperarousal: This can manifest as heightened anxiety, increased irritability, difficulty sleeping, and an exaggerated startle response.
- Dissociation: Some individuals may experience dissociative symptoms, where they feel detached from their body or reality as a way of coping with the trauma.
- Emotional Dysregulation: Difficulty regulating emotions can result in mood swings, anger outbursts, or emotional instability.
- Hypervigilance: An ongoing state of alertness and vigilance, where individuals are constantly on guard, scanning their environment for potential threats.
- Impaired Self-Esteem: Persistent trauma can lead to feelings of worthlessness, shame, and self-blame, often as a result of internalizing the trauma.
- Guilt and Responsibility: Many individuals experiencing Recurrent trauma may feel an overwhelming sense of guilt, believing they should have done more to prevent or escape the traumatic situation.
- Social Isolation: Difficulty forming and maintaining relationships, leading to withdrawal from social activities and a sense of isolation.
These symptoms underscore the complex and lasting effects of chronic trauma on an individual’s mental and emotional well-being.
The Impact of Chronic Trauma on Mental Health
- Anxiety and Depression: Chronic trauma can heighten the risk of developing anxiety disorders and depressive disorders, leading to persistent feelings of fear, sadness, and hopelessness.
- Dissociation: Individuals may experience dissociation, a coping mechanism where they mentally detach from reality to protect themselves from overwhelming emotions.
- Difficulty Trusting Others: Trust issues can arise due to experiences of betrayal or abandonment, making it challenging to form and maintain healthy relationships.
- Self-Esteem Issues: Persistent trauma can erode a person’s sense of self-worth and self-esteem, leading to feelings of inadequacy and low self-confidence.
- Emotional Dysregulation: Difficulty in regulating emotions can lead to intense mood swings, impulsive behavior, and difficulty coping with stress.
- Issues with Boundaries: Establishing and maintaining healthy boundaries can be a struggle for individuals who have experienced chronic trauma.
In conclusion, chronic trauma has far-reaching and enduring effects on an individual’s mental health. It can lead to complex post-traumatic stress disorder (C-PTSD), anxiety, depression, and a range of emotional and psychological challenges.