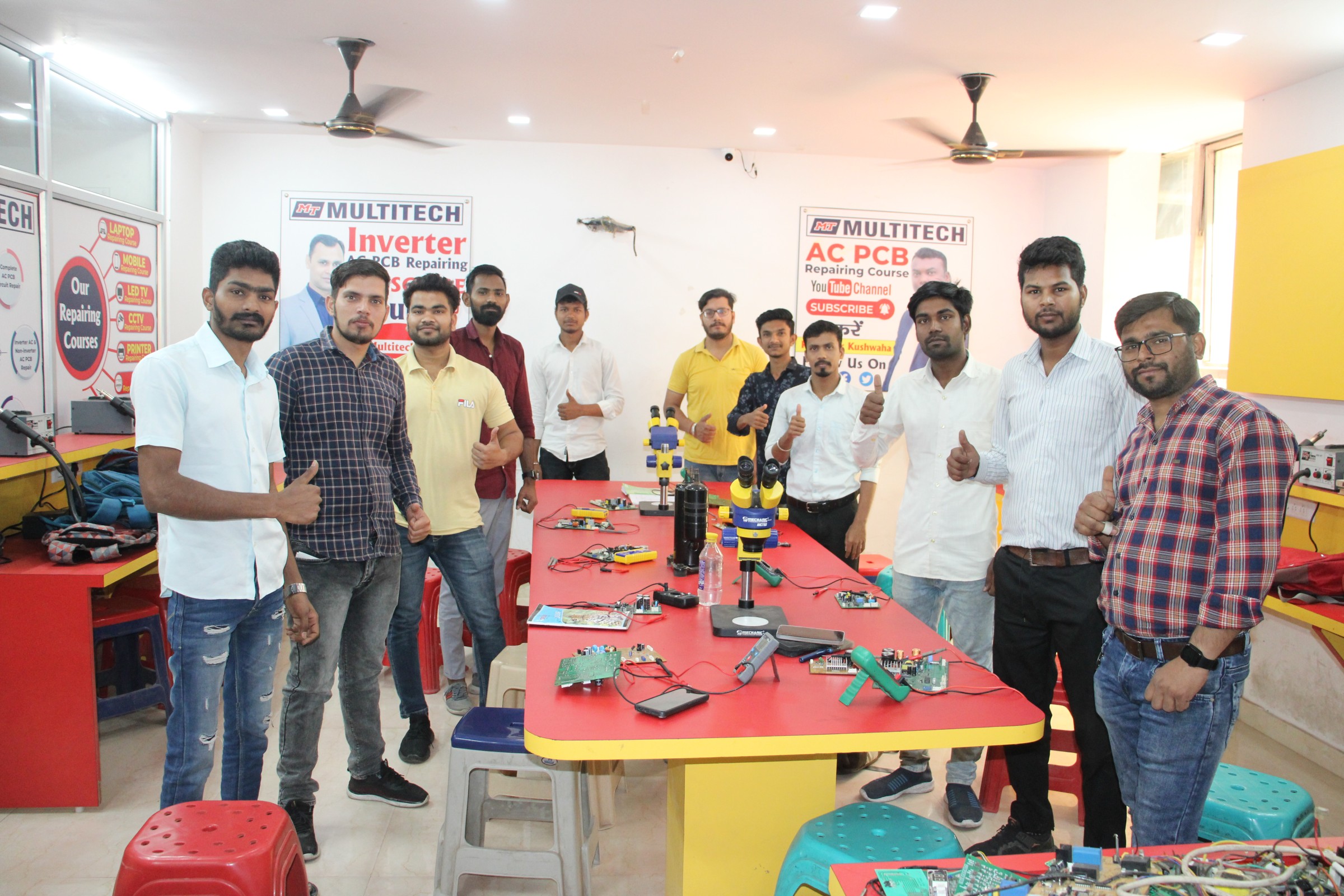
In today’s fast-paced world, where comfort and convenience are paramount, air conditioning systems have become a staple in households, offices, and industries. These systems, however, are complex machines with intricate components, and like any technology, they can sometimes malfunction. This is where the importance of AC PCB Repairing Courses becomes evident.
Why AC Repairing Courses are Essential
The necessity of AC Repairing Courses is grounded in the growing ubiquity of air conditioning systems. These systems have transitioned from being a luxury to an essential part of our lives, making the role of AC technicians indispensable. AC Repairing Courses are essential for several reasons:
-
Rising Demand: The increasing use of air conditioning systems results in a corresponding increase in the need for technicians who can maintain and repair them. This high demand creates numerous opportunities for certified professionals.
-
Complexity of Systems: Modern air conditioners are sophisticated machines, incorporating advanced technologies and electronic components. Repairing them requires specialized knowledge and skills.
-
Energy Efficiency: AC systems are evolving to be more energy-efficient. Repair technicians must stay up-to-date with these advancements, making professional training crucial.
-
Quality Assurance: Repairing air conditioners without proper training can lead to costly mistakes. AC Repairing Courses ensure that technicians can efficiently and effectively diagnose and repair AC units, providing quality assurance to customers.
Understanding the Basics of PCBs
To delve into the world of AC PCB Repairing, it’s essential to grasp the basics of Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs). PCBs play a vital role in the functioning of air conditioners, as they control and coordinate various components. In these courses, students learn about:
PCB Components: Understanding the components, circuits, and connections on a PCB is fundamental. This includes resistors, capacitors, diodes, transistors, and integrated circuits.
PCB Schematics: Students are taught how to read and interpret PCB schematics, which are essential for troubleshooting and repairing AC units.
PCB Design: Some courses also cover the design aspect of PCBs, enabling students to design their own PCBs for specific applications.
Tools and Equipment for AC PCB Repair
Repairing air conditioners requires specific tools and equipment to diagnose and fix issues accurately. Some of the essential tools and equipment include:
Multimeter: A multimeter is used to measure voltage, current, and resistance in various components.
Soldering Iron and Station: These are required for soldering and desoldering components on the PCB.
Breadboard and Power Supply: These tools are used for testing circuits before making permanent connections on the PCB.
Oscilloscope: An oscilloscope is essential for analyzing electronic signals on the PCB.
Diagnostic Software: Some modern AC units require the use of diagnostic software to identify issues, making it vital for technicians to be proficient with this technology.
Diagnosis and Troubleshooting
Diagnosis and troubleshooting form a core part of AC PCB Repairing Courses. Students learn how to identify common issues, such as compressor problems, refrigerant leaks, or electrical faults. They also gain the skills to troubleshoot these issues systematically, ensuring efficient and effective repairs.
The diagnostic process typically involves:
Visual Inspection: Inspecting the AC unit for visible damage or irregularities.
Testing Components: Using tools like the multimeter and oscilloscope to test various components for faults.
Fault Code Analysis: Interpreting error codes displayed on the AC unit’s control panel.
Systematic Approach: Teaching students a structured approach to identify and rectify issues step by step.
By mastering diagnostic techniques, technicians can quickly identify problems and provide accurate solutions.
Theoretical Foundation: Electronic Components
A strong theoretical foundation is crucial for AC PCB Repairing. This section of the course delves into electronic components, their functions, and their roles within the PCB. Some of the key components covered include:
Resistors: Understanding how resistors control the flow of current.
Capacitors: Learning about capacitors and their ability to store and release electrical energy.
Diodes: Exploring diodes and their role in allowing current to flow in one direction.
Transistors: Understanding transistors, which are used for amplification and switching purposes.
Integrated Circuits: Gaining knowledge about integrated circuits, which contain multiple components in a single package.
Having a solid understanding of these electronic components is essential for efficient repairs and maintenance.
Hands-On Training: Practical Application
Deconstructing and Assembling AC Units: Students learn how to safely take apart an air conditioner, diagnose issues, and reassemble it after repair.
Soldering and Desoldering: Proper soldering techniques are essential for replacing damaged components on the PCB.
Troubleshooting Simulators: Some institutes use simulators to mimic real-world scenarios, allowing students to practice diagnosing and repairing various faults.
This hands-on experience is invaluable, as it bridges the gap between theory and practice, preparing students to tackle real-world AC repair challenges effectively.
Inverter AC PCB Repairing
Inverter air conditioners have gained popularity for their energy efficiency and precise temperature control. Repairing inverter ACs requires a specialized skill set. In this section, students are introduced to:
Inverter Technology: Understanding how inverter technology works to adjust the compressor’s speed for optimal cooling.
Common Inverter AC Issues: Learning to diagnose and address specific problems that may arise in inverter AC units.
Testing and Calibration: Gaining the ability to calibrate and test inverter modules for optimal performance.
This specialization in inverter AC repair ensures that technicians can handle the latest advancements in the HVAC industry.
Scope and Opportunities
The completion of an AC PCB Repairing Course opens a world of opportunities for graduates. Job prospects include:
AC Technician: Many graduates become AC technicians, offering repair and maintenance services to residential and commercial clients.
Entrepreneurial Ventures: Some individuals choose to start their own AC repair businesses, catering to a niche market or offering specialized services.
HVAC Companies: Graduates can find employment with HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) companies, where they may work on various AC systems in diverse settings.
How to Choose the Right Institute
Selecting the right institute is critical for a successful career in AC PCB Repairing. Consider the following factors when choosing an institute:
Accreditation: Ensure that the institute is recognized by relevant industry bodies.
Faculty Expertise: Research the qualifications and experience of the teaching staff.
Infrastructure: Check if the institute has state-of-the-art equipment and labs for practical training.
Placement Assistance: Inquire about the institute’s placement assistance programs.
Course Duration: Assess whether the course duration aligns with your goals and availability.
Duration and Fees
The duration and fees of AC PCB Repairing Courses can vary from one institute to another. On average, these courses range from 3 to 6 months. As for the fees, they depend on factors like the institute’s reputation, course depth, and whether any additional materials are included. It’s essential to research and compare options to find a course that fits your budget and schedule.
Certification and Accreditation
Certification is a significant aspect of an AC PCB Repairing Course. Graduates should receive certification from recognized industry bodies, which adds credibility to their skills. Some institutes may offer accredited programs that align with industry standards.
Career Prospects
Upon completing an AC PCB Repairing Course, graduates can explore numerous career prospects. These include:
AC Technician: Providing repair and maintenance services to residential and commercial clients.
Service Center Technician: Working at service centers for renowned AC brands.
Entrepreneur: Starting their own AC repair business, which can be lucrative with the right skills and customer service.
HVAC Technician: Joining HVAC companies specializing in climate control systems.
In conclusion, AC PCB Repairing Courses open doors to a fulfilling and rewarding career in the HVAC industry. With a strong foundation in theory, hands-on practical experience, and a wide range of career opportunities, graduates are well-prepared to excel in this dynamic field.
FAQs
Is prior knowledge of electronics required for AC PCB Repairing Courses?
No, these courses are designed to accommodate individuals with varying levels of prior knowledge in electronics.
How long does it typically take to complete an AC PCB Repairing Course?
The duration varies but usually ranges from 3 to 6 months, depending on the institute and the depth of the course.
What are the job prospects after completing an AC PCB Repairing Course?
Graduates can work as AC technicians, start their own repair businesses, or even join HVAC companies.
Do AC Repairing Institutes in Delhi offer online courses?
Yes, many institutes now offer online courses, providing flexibility to students.
Is financial assistance available for these courses?
Some institutes may offer scholarships or installment payment options to make these courses more accessible.